Ensuring your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is essential for inclusivity and compliance. This tutorial guides you through analyzing accessibility using WCAG guidelines, tools, and testing methods. Follow these steps to identify issues and make improvements.
Step 1: Understand WCAG Guidelines
Familiarize yourself with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Focus on levels A, AA, and AAA, covering principles like perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. Analyze your site’s compliance by reviewing criteria such as alt text for images and keyboard navigation.
Use resources like the WCAG quick reference to map out requirements.
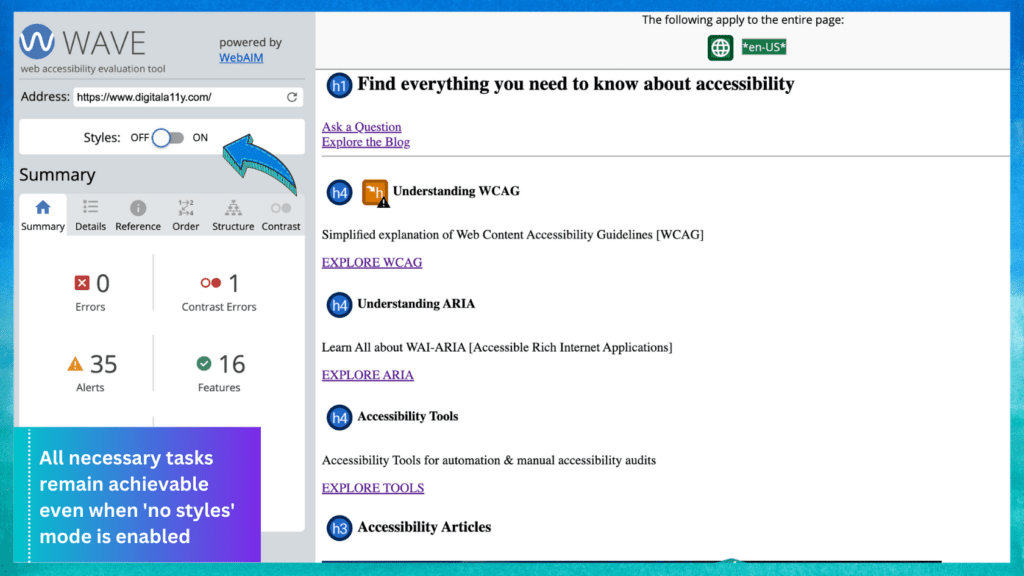
Step 2: Use Automated Testing Tools
Employ tools like WAVE, axe, or Lighthouse to scan your pages. Input your URL and run the analysis to detect issues like missing alt attributes or low contrast ratios.
Review the results, categorize errors, and note suggestions for fixes.

Step 3: Perform Manual Checks
Automated tools miss some issues, so manually test elements. Check color contrast with tools like WebAIM’s checker, ensure logical heading structure, and verify form labels.
Simulate user experiences, like navigating without a mouse.
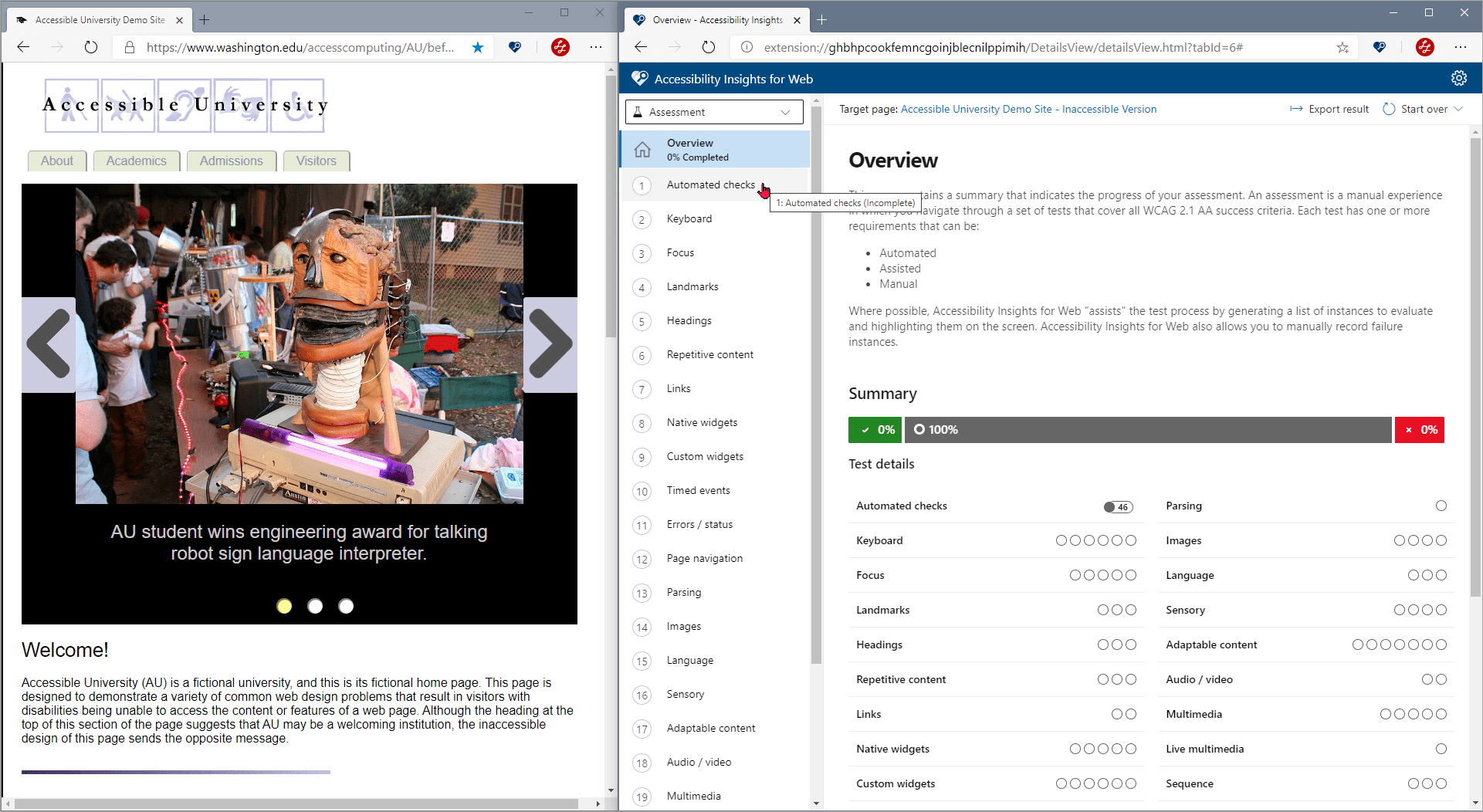
Step 4: Test with Assistive Technologies
Use screen readers like NVDA or VoiceOver to analyze how content is read aloud. Test with keyboard-only navigation and zoom features to ensure usability.
Gather feedback from users with disabilities for real-world insights.
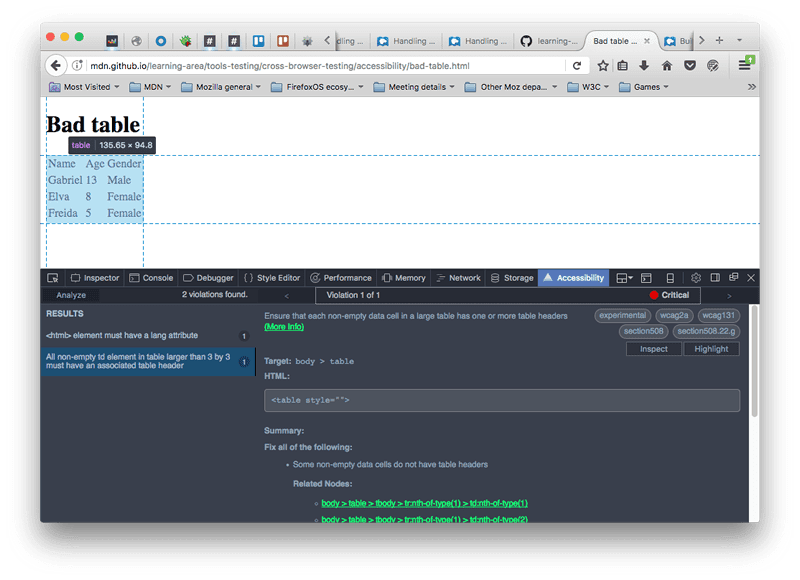
Step 5: Implement Fixes and Retest
Prioritize issues, apply changes like adding ARIA roles or improving semantics, then retest with tools and manual methods. Document your process for ongoing maintenance.
Regular audits keep your site accessible. For more tutorials, visit appstuf.com.