Quantum computing is advancing rapidly, promising to solve complex problems beyond classical computers’ reach. This overview highlights recent breakthroughs, from enhanced algorithms to scalable systems and collaborative efforts, based on current reports. These developments could revolutionize fields like drug discovery, cryptography, and materials science.
Google’s Quantum Echoes Algorithm on Willow
Google has achieved a significant milestone with its Willow quantum chip and the Quantum Echoes algorithm, enabling computations 13,000 times faster than classical supercomputers for certain tasks. This verifiable quantum advantage opens doors to unprecedented scientific analysis and discoveries.
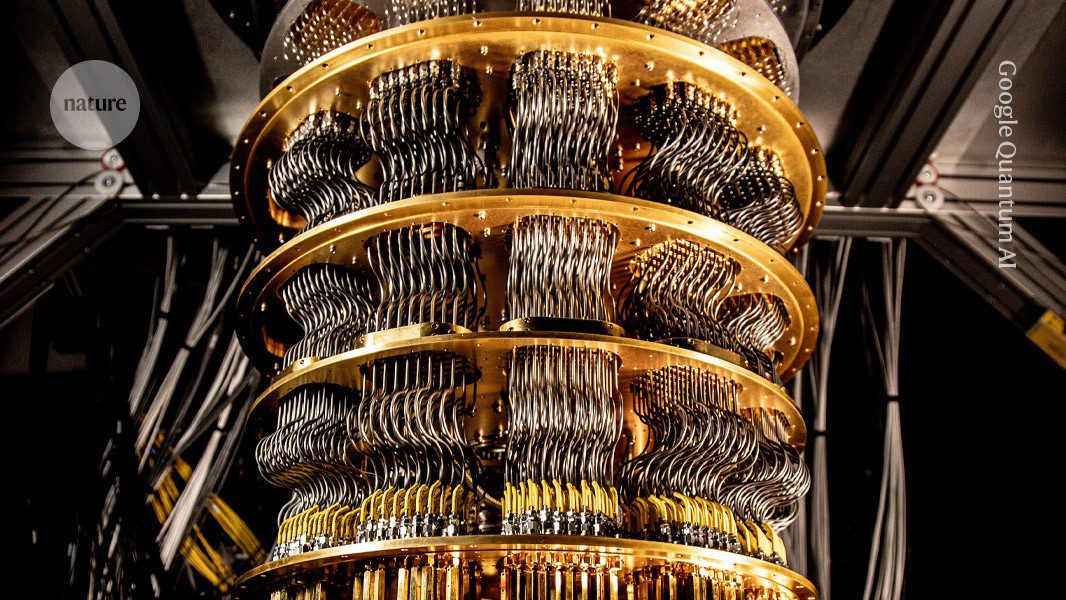
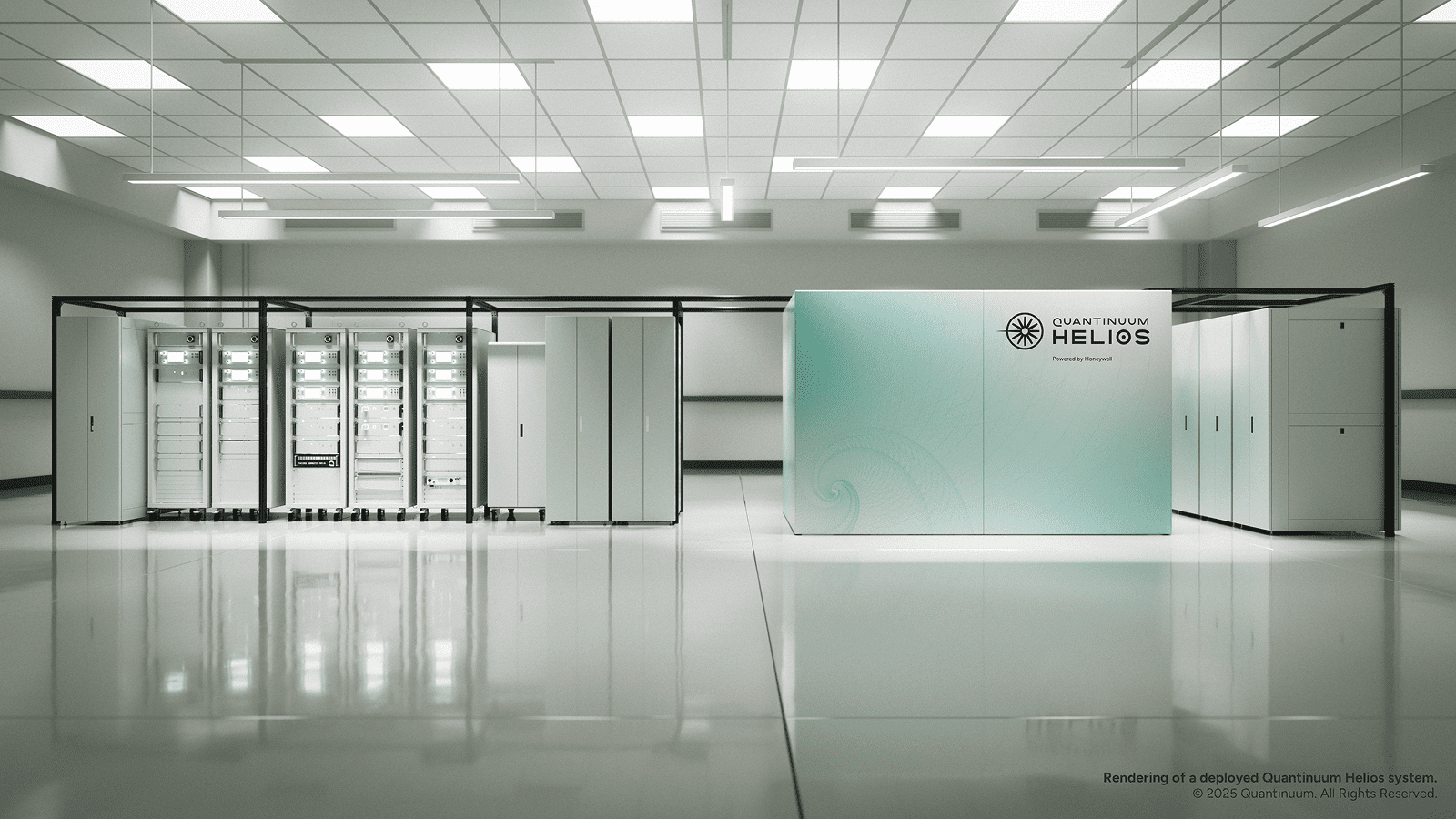
Helios: Record-Breaking Quantum Machine
Scientists have introduced Helios, a 98-qubit system claimed to be the most powerful quantum computer available, outperforming others in benchmark tasks. Its design focuses on stability and scalability, pushing the boundaries of practical quantum applications.

Long-Lived Qubits for Error Correction
A major advancement in qubit longevity addresses error correction challenges, with new architectures like IBM’s planned Starling system enabling more reliable computations. This breakthrough could lead to fault-tolerant quantum machines sooner than expected.
Quantum Scaling Alliance Launch
HPE and partners have formed the Quantum Scaling Alliance to integrate quantum computing with high-performance computing, aiming for breakthroughs in areas like semiconductor manufacturing and sustainable materials. This collaboration highlights the push toward hybrid systems for real-world problems.

Other Notable Advances
Additional progress includes NIST and SQMS improvements in qubit coherence for better performance, and McKinsey’s insights on quantum tech transitioning from concept to reality, covering computing, sensing, and communication. Equal1’s hybrid systems with the European Space Agency and Chicago’s new quantum facility signal growing infrastructure support.